Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
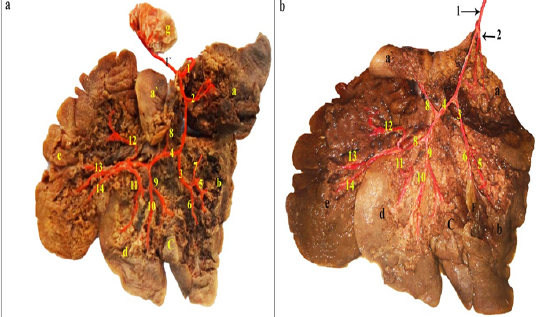
a and b: Visceral surface of the rabbit liver dissected- showing the intrahepatic branches of the hepatic artery- injected with colored latex neoprene.
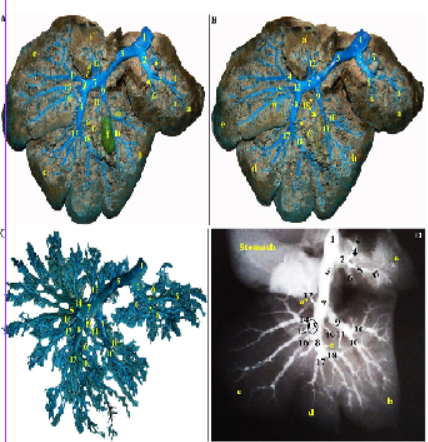
Photographs showing the intrahepatic branches of the portal vein in Rabbit. (A and B): Visceral surface of the rabbit liver – dissected- injected with colored latex neoprene. A. Gall bladder in situ (injected), B. Gall bladder was removed. (C) colored latex neoprene cast– caudal view. (D) Radiographic X-ray film.
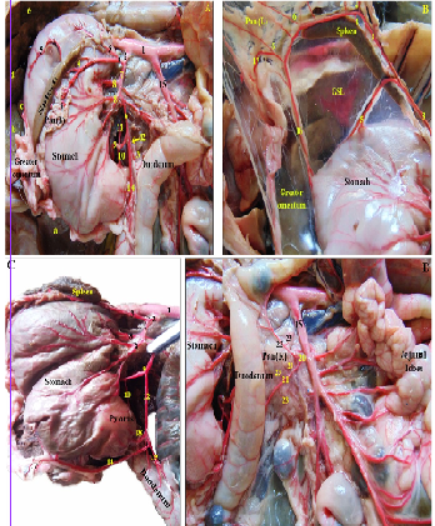
Photographs showing the blood supply of the pancreas and spleen in rabbit -dissected- injected with colored latex neoprene. (A): branches of the celiac trunk. (B): branches of the splenic artery. (C,D): Photographs showing the arterial supply of the body and right pancreatic lobe by branches of the gastroduodenal and caudal pancreaticoduodenal arteries.
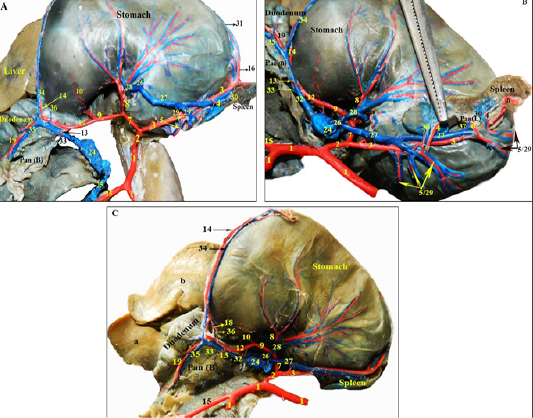
Photographs showing the branches of the extrahepatic tributaries of the portal vein draining the pancreas and spleen in rabbit, alongside their satellite arteries rabbit -dissected- injected with colored latex neoprene. (A): the extrahepatic tributaries of the portal vein, notice the gastrosplenic vein is cut and reflected. (B): the splenic vein and its branches. (C): branches of the gastroduodenal vein.
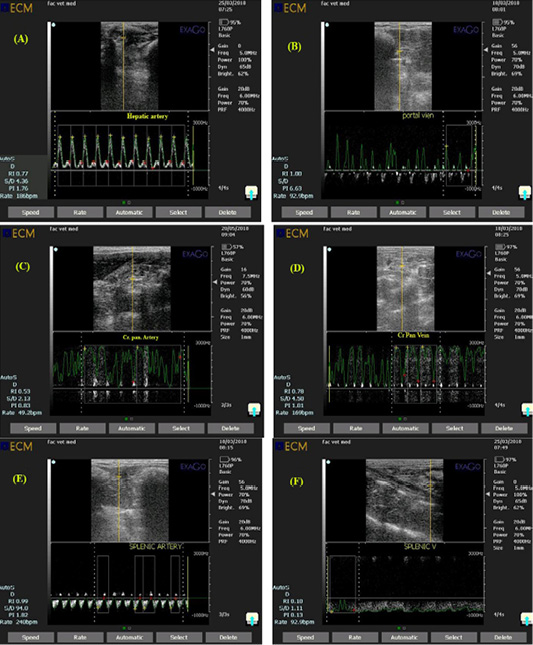
Ultrasonogram showing pulsed wave doppler mode of rabbit hepatic artery (A), portal vein (B), Cranial pancreaticoduodenal artery (C), Cranial pancreaticoduodenal vein (D), splenic artery (E) and Splenic vein (F) with a a gate opened in the known artery to measure amount of blood flow and a gate opened in the known vein to measure amount of blood drainage.