Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
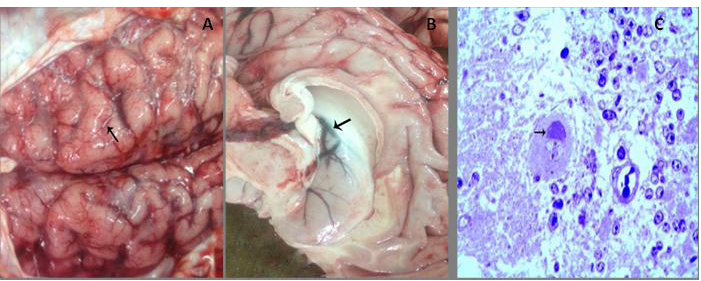
Gross examination and Toluidine blue staining of infected brain tissues of buffalo A) Congestion of meningeal blood vessels with flattening gyri and narrowing sulci (arrow); B) Congestion and edema in the wall of the lateral ventricle (arrow) with bulging into the lumen. C) Bluish stained Negri body forming a cap over the nucleus with interstitial edema. (Toluidine blue, x400)
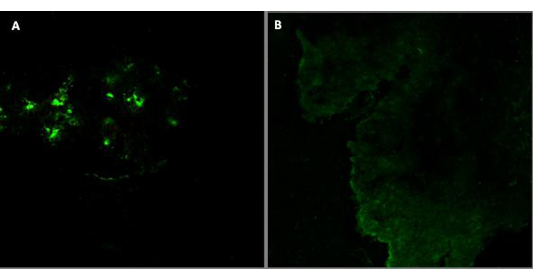
Detection of rabies virus antigen in the brain of infected buffalo by FAT A) Positive reaction in infected brain tissues; B) Control brain tissue of non-infected tissue
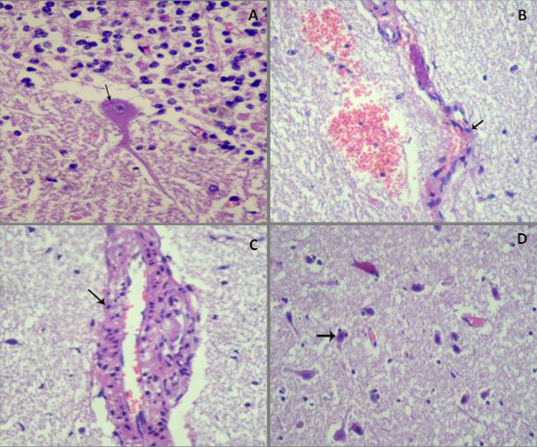
Histopathological examination of infected brains of buffalo by Rabies virus A) Esinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion body (Negri body) around nucleus of Purkinje cell, (HE, x400); B) Endothelial cells become round (arrow) with necrosis and desquamation, perivascular edema and hemorrhage, (HE, x100); C) Swollen endothelial lining of cerebral capillaries and perivascular edema with lymphohistiocytic infiltration in its wall (arrow), (HE, x400); D) Edema of neuropil and status spogiosus, in addition to diffuse neuronal necrosis and satellitosis (arrow) ((HE,x100)
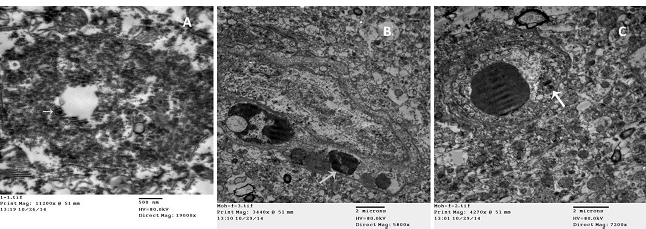
Electron microscopic examination of infected brains of Buffalo by Rabies virus A) Electron dense intracytoplasmic inclusion with bullet shape viral particles (arrow) (TEM); B) Clumped chromatin of endothelial cell (arrow), with vasogenic edema (TEM); C) Chromatolysis and vacuolation of endothelial cell (arrow), with vasogenic edema (TEM).